
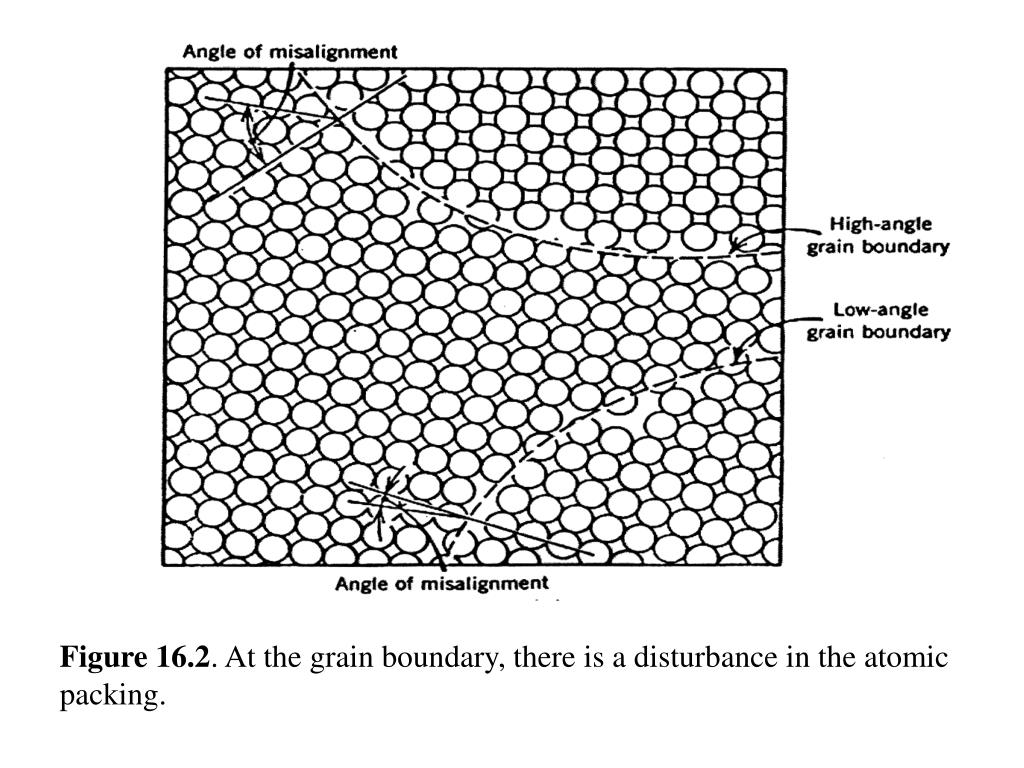
Soft magnetic Fe-Si steels, semi-amorphous steels, and iron-based metallic glasses for low-loss electrical motors and wind energy generators radiation resistant steels for nuclear and fusion power ExamplesĪre advanced Fe-Cr steels for high-temperature applications in emission-reduced turbines weight reduced and ultra high strength Fe-Mn steels for light-weight and yet passenger-protecting mobility Strong, damage-tolerant, and functional steels are the backbone for multiple innovations in the fields of energy, transportation, health, safety, machinery, and industrial infrastructure. On the decoration driving forces phenomenologically described by the Gibbs adsorption isotherm, are referred to as equilibrium segregation engineering. These effects, which are essentially built When aiming at the local modification of the microstructure, this SE approach isĪpplied in such a way that these critical conditions are only fulfilled at the lattice defect regions, leaving the adjacent matrix essentially unaffected. Where the sample is heated into a phase regime which is intercritical at the decorated and distorted defect region. On the one hand, and the locally altered chemical composition at these defects on the other hand, can initiate structural transitions, solute ordering, and phase transformation states in such cases The resulting combinations of local strain fields at such lattice defects Traps, thus, entailing strong solute segregation when heat treated into regimes that allow for sufficient solute diffusion. In this case the targeted segregation engineering effects occur in a spatially confined manner, namely, at lattice defects, which act as efficient and highly thermodynamically attractive solute Theoretical analysis of grain boundary segregation phenomena is conducted on the basis of the Gibbs and McLean isotherm approaches and also in Necessity and challenge in coupling such near-atomic chemical interface characterization via atom probe tomography with structural analysis via electron microscopy of the same material region isĭiscussed and corresponding examples are presented.

This webpage gives a little introduction to the current state of chemical grain boundary analysis in advanced alloys by use of atom probe tomography. In this context segregation of soluteĪtoms to grain boundaries plays a major role. High strength alloys: Their structural and chemical state can be a decisive factor whether the bulk material reacts brittle or ductile against external loads. This applies particularly to interfaces in Segregation Engineering in Additive ManufacturingĪdvanced metallic alloys for structural and functional applications can be manipulated down to the nanometer scale, for instance through heat treatments.Combinatorial discovery of high-entropy alloys.Bi-directional TRIP High Entropy Alloys.Aluminium alloys for aerospace applications.Copper alloys and Copper-Nano-Composites.Hydrogen embrittlement of medium Mn steel.Soft magnetic steels for electromobility.Joint crystal plasticity and phase field models.Phase field and Ginzburg-Landau modeling.Large scale crystal plasticity amd ansiotropy simulation.Dislocation-based Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method.Crystal Plasticity Finite Element Method.Chemistry dependence of constitutive models.Recrystallization and grain growth simulation.Field Ion Microscopy - Mapping single atoms.Atom probe tomography on metallic glass.Atom probe tomography cryogenic UHV prep.Digital Image Correlation and crystal plasticity simulation.Digital Image Correlation for multiphase alloys.What is red mud and why is it dangerous?.Sustainable steel production: Strip casting of steel.Green Steel: Reduction of iron ore by hydrogen plasma.Green Steel: Direct reduction of iron ore with hydrogen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
